Ignite Chain
Introduction
Ignite is a blockchain to help launch Cosmos SDK-based blockchains.
Using Cosmos SDK and Ignite CLI, developers can quickly create a crypto application that is decentralized, economical for usage, and scalable. The Cosmos SDK framework allows developers to create sovereign application-specific blockchains that become part of the wider Cosmos ecosystem. Blockchains created with Cosmos SDK use a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus protocol that requires validators to secure the chain.
Even though tools like Ignite CLI simplify the development of a Cosmos SDK blockchain, launching a new chain is a highly complex process. One of the major challenges of developing and launching your own sovereign blockchain is ensuring the security of the underlying consensus. Since Cosmos SDK chains are based on the PoS consensus, each blockchain requires initial coin allocations and validators before they can be launched, which presents developers with significant challenges, such as determining their chain's tokenomics or coordinating a robust validator set.
The initial coin allocations and validators are described in a JSON-formatted genesis file that is shared among all initial nodes in the network. This genesis file defines the initial state of the application. Based on PoS, secure chains require the initial allocation of coins to be well distributed so that no single validator holds more than 1/3 of all tokens and receives a disproportionate amount of voting power.
Along with ensuring the security of the underlying consensus, another highly difficult task in launching a new blockchain is attracting a diverse set of validators for the genesis file. Many promising projects fail to capture the attention of a sufficient number of trustworthy validators to secure their chains due to a lack of resources or experience.
The Ignite Chain has, therefore, been conceived to facilitate the launch of Cosmos SDK blockchains by helping developers to navigate the complexities of launching a blockchain and coordinate the genesis of a new chain. Using the decentralized nature of blockchain, Ignite's coordination features help blockchain builders connect with validators and investors, speeding up the time to market of their projects and chances of success.
Commands to interact with Ignite Chain are integrated into Ignite CLI and allow launching chains from it. Integration with Ignite Chain allows the CLI to support the developer in the entire lifecycle of realizing a Cosmos project, from the development and experimentation of the blockchain to the launch of its mainnet.
What is Ignite Chain
Ignite Chain is a secure platform that simplifies the launch of Cosmos SDK-based chains, lending vital resources and support at the coordination, preparation, and launch stages. Ignite provides the tools that blockchain projects need to overcome the complexities of launching their chain, from validator coordination and token issuance to fundraising and community building.
Ignite facilitates the launch of new chains with an overall launch process during three phases:
- Coordination
- Preparation
- Launch
To reduce friction at each phase, Ignite provides an immutable and universal database for validator coordination.
In the future, Ignite will also offer:
- Token issuance: Ignite allows the issuance of tokens (called vouchers) that represent a share allocation of a future mainnet network
- A fundraising platform for selling vouchers
- A permissionless framework to reward validator activities on a launched testnet network
Validator coordination
To launch a chain in the Cosmos ecosystem, the validators must start nodes that connect to each other to create the new blockchain network. A node must be started from a file called the genesis file. The genesis file must be identical on all validator nodes before the new chain can be started.
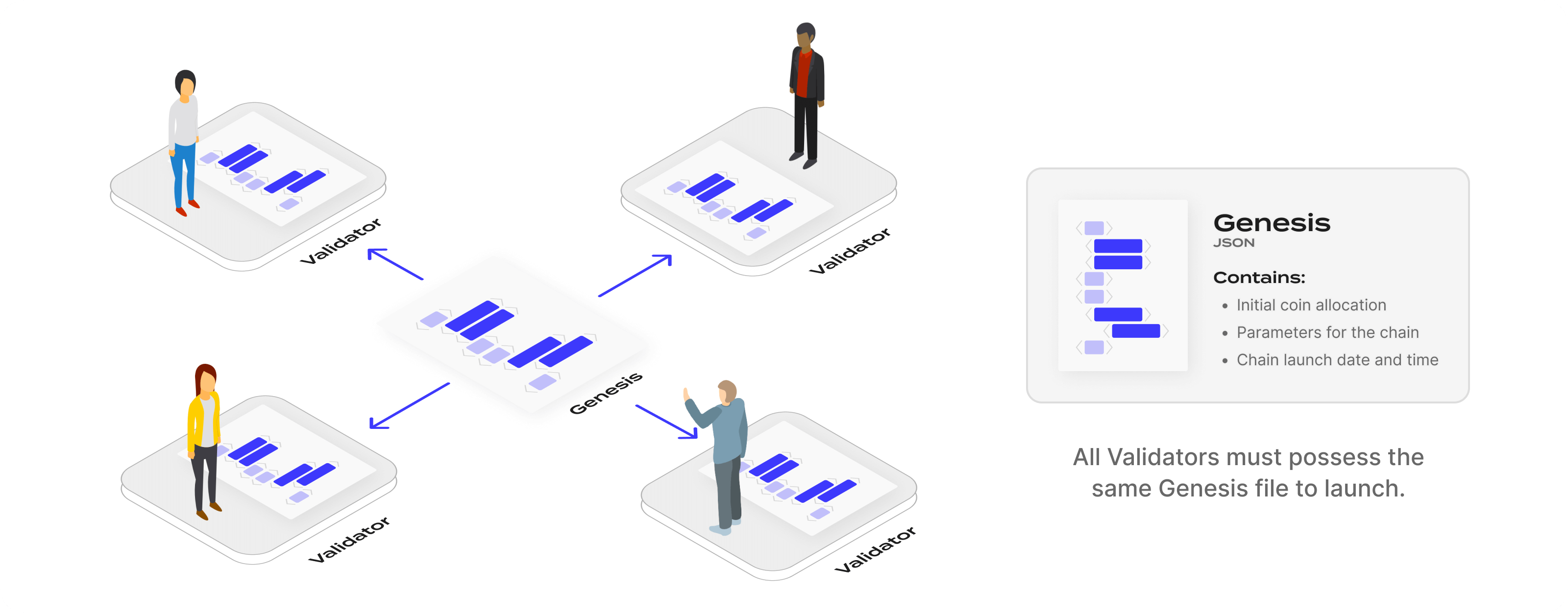
The JSON-formatted genesis file contains information on the initial state of the chain, including coin allocations, the list of validators, various parameters for the chain like the maximum number of validators actively signing blocks, and the specific launch time. Because each validator has the same genesis file, the blockchain network starts automatically when the genesis time is reached.
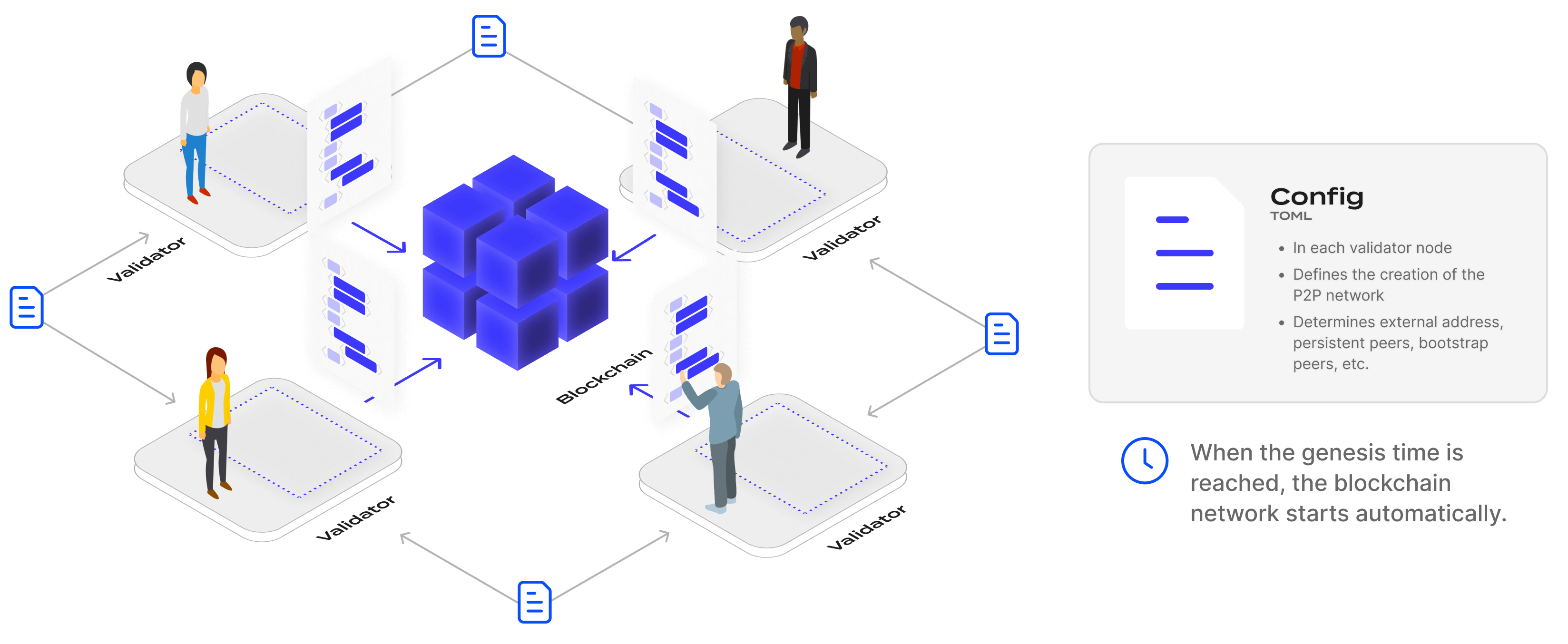
Ignite as a coordination source of truth
Ignite Chain acts as a source of truth for new chains to coordinate a validator set and for validators to generate the genesis for a chain launch. The blockchain doesn’t directly store the final genesis file in its own ledger but rather stores information that allows generating the genesis file in a deterministic manner.
The information stored on Ignite that supports deterministic generation of the genesis file for a specific chain launch is referred to as the launch information. When creating a new chain on Ignite, the coordinator provides the initial launch information. Then, through on-chain coordination, this launch information is updated by interacting with the blockchain by sending messages. When the chain is ready to be launched, the genesis file is generated by calling a genesis generation algorithm that uses the launch information.
GenesisGenerate(LaunchInformation) => genesis.json
The genesis generation algorithm is officially and formally specified. The official implementation of the genesis generation algorithm is developed in Go using Ignite CLI. However, any project is free to develop its own implementation of the algorithm as long as it complies with the specification of the algorithm.
The genesis generation algorithm is not part of the on-chain protocol. In order to successfully launch a new chain, all validators must use the algorithm to generate their genesis using the launch information. The algorithm deterministically generates the genesis from the launch information that is stored on the Ignite chain.
If any element of the launch information is censored, for example, removing an account balance, the launched chain reputation is negatively impacted and implies that the majority of validators agree on not using:
- The tamper-proof launch information
- The official genesis generation algorithm
Outside of the genesis generation, the genesis generation algorithm specification gives guidance on how to set up your network configuration. For example, the launch information can contain the addresses of the persistent peers of the blockchain network.
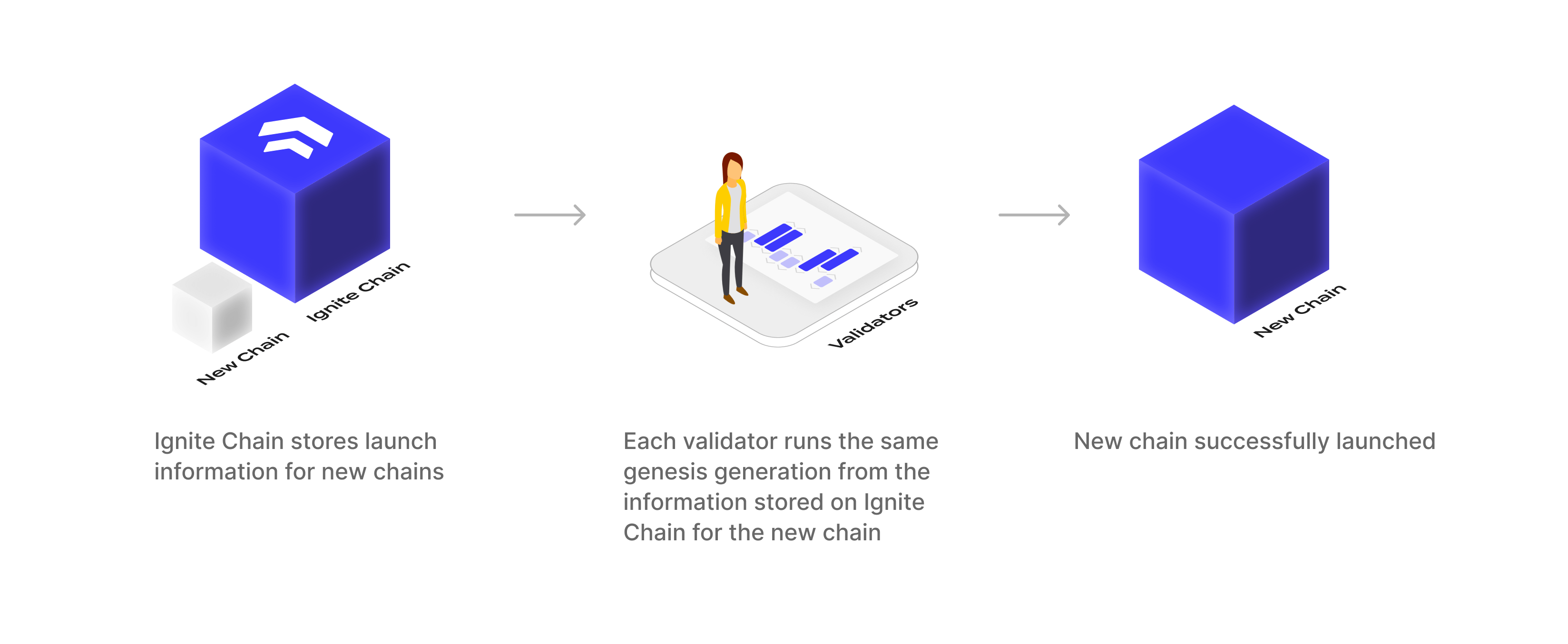
Launch information
Launch information can be created or updated in three different ways:
- Defined during chain creation but updatable by the coordinator after creation
- Determined through coordination
- Determined through specific on-chain logic not related to coordination
1 - Launch information determined during chain creation:
GenesisChainID: The identifier for the networkSourceURL: The URL of the git repository of the source code for building the blockchain node binarySourceHash: The specific hash that identifies the release of the source codeInitialGenesis: A multiformat structure that specifies the initial genesis for the chain launch before running the genesis generation algorithm
2 - Launch information determined through coordination:
GenesisAccounts: A list of genesis accounts for the chain, comprised of addresses with associated balancesVestingAccounts: A list of genesis accounts with vesting optionsGenesisValidators: A list of the initial validators at chain launchParamChanges: A list of module param changes in the genesis state
3 - Launch information determined through on-chain logic:
GenesisTime: The timestamp for the network start, also referred to as LaunchTime
Initial genesis
The launch information contains the initial genesis structure. This structure provides the information for generating the initial genesis before running the genesis generation algorithm and finalizing the genesis file.
The initial genesis structure can be:
DefaultGenesis: the default genesis file is generated by the chain binary init commandGenesisURL: the initial genesis for a chain launch is an existing genesis file that is fetched from a URL and then modified with the required algorithm - this initial genesis type should be used when the initial genesis state is extensive, containing a lot of accounts for token distribution, containing records for an airdropGenesisConfig: the initial genesis for a chain launch is generated from an Ignite CLI config that contains genesis accounts and module parameters - this initial genesis type should be used when the coordinator doesn’t have extensive state for the initial genesis but some module parameters must be customized. For example, the staking bond denom for the staking token
Coordination process
The coordination process starts immediately after the chain is created and ends when the coordinator triggers the launch of the chain.
The launch information is updated during the coordination process.
During the coordination process, any entity can send requests to the network. A request is an object whose content specifies updates to the launch information.
The chain coordinator approves or rejects the requests:
- If a request is approved, the content is applied to the launch information
- If the request is rejected, no change is made to the launch information
The request creator can also directly reject or cancel the request.
Each chain contains a request pool that contains all requests. Each request has a status:
- PENDING: Waiting for the approval of the coordinator
- APPROVED: Approved by the coordinator, its content has been applied to the launch information
- REJECTED: Rejected by the coordinator or the request creator
Approving or rejecting a request is irreversible. The only possible status transitions are:
- PENDING to APPROVED
- PENDING to REJECTED
To revert the effect on launch information from a request, a user must send the eventual opposite request (example: AddAccount → RemoveAccount).
Since the coordinator is the sole approver for requests, each request created by the coordinator is immediately set to APPROVED and its content is applied to the launch information.
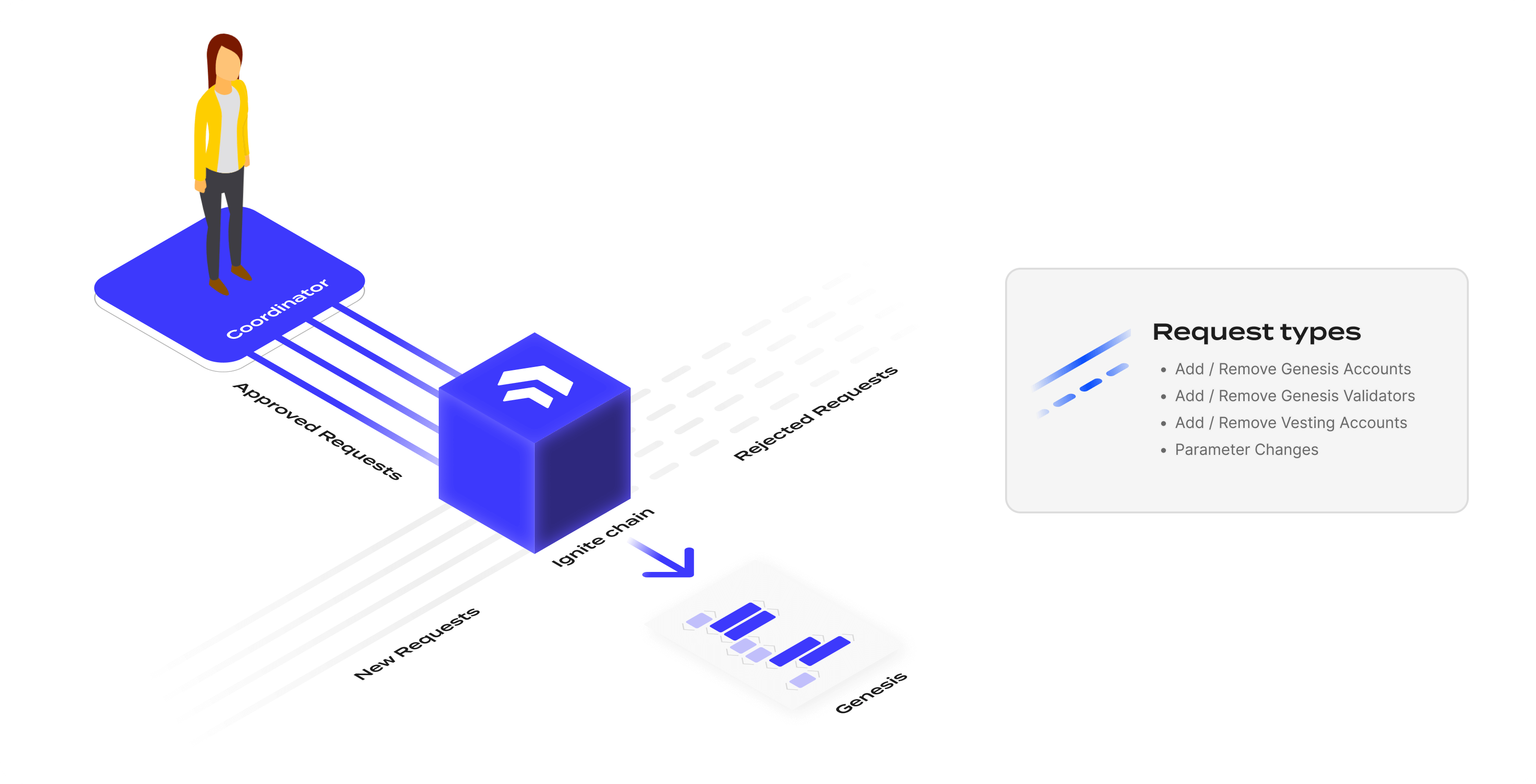
Available requests
Six types of requests can be sent to the Ignite chain:
AddGenesisAccountAddVestingAccountAddGenesisValidatorRemoveAccountRemoveValidatorChangeParam
AddGenesisAccount requests a new account for the chain genesis with a coin balance. This request content is composed of two fields:
- Account address, must be unique in launch information
- Account balance
The request automatically fails to be applied if a genesis account or a vesting account with an identical address is already specified in the launch information.
AddVestingAccount requests a new account for the chain genesis with a coin balance and vesting options. This request content is composed of two fields:
- Address of the account
- Vesting options of the account
The currently supported vesting option is delayed vesting where the total balance of the account is specified and a number of tokens of the total balance of the account are vested only after an end time is reached.
The request automatically fails to be applied if a genesis account or a vesting account with an identical address is already specified in the launch information.
AddGenesisValidator requests a new genesis validator for the chain. A genesis validator in a Cosmos SDK blockchain represents an account with an existing balance in the genesis that self-delegates part of its balance during genesis initialization to become a bonded validator when the network starts. In most cases, the validator must first request an account with AddGenesisAccount before requesting to be a validator, unless they already have an account with a balance in the initial genesis of the chain.
Self-delegation during genesis initialization is performed with a Cosmos SDK module named genutils. In the genesis, the genutils module contains objects called gentx that represent transactions that were executed before the network launch. To be a validator when the network starts, a future validator must provide a gentx that contains the transaction for the self-delegation from their account.
The request content is composed of five fields:
- The gentx for the validator self-delegation
- The address of the validator
- The consensus public key of the validator node
- The self-delegation
- The peer information for the validator node
The request automatically fails to be applied if a validator with the same address already exists in the launch information.
RemoveAccount requests the removal of a genesis or vesting account from the launch information. The request content contains the address of the account to be removed. The request automatically fails to be applied if no genesis or vesting account with the specified address exists in the launch information.
RemoveValidator requests the removal of a genesis validator from the launch information. The request content contains the address of the validator to be removed. The request automatically fails to be applied if no validator account with the specified address exists in the launch information.
ChangeParam requests the modification of a module parameter in the genesis. Modules in a Cosmos SDK blockchain can have parameters that will configure the logic of the blockchain. The parameters can be changed through governance once the blockchain network is live. During the launch process, the initial parameters of the chain are set in the genesis.
This request content is composed of three fields:
- The name of the module
- The name of the parameter
- The value of the parameter represented as generic data
Request validity
Some checks are verified on-chain when applying a request. For example, a genesis account can’t be added twice. However, some other validity properties can’t be checked on-chain. For example, because a gentx is represented through a generic byte array in the blockchain, an on-chain check is not possible to verify that the gentx is correctly signed or that the provided consensus public key that is stored on-chain corresponds to the consensus public key in the gentx. This gentx verification is the responsibility of the client interacting with the blockchain to ensure the requests have a valid format and allow for the start of the chain. Some validity checks are specified in the genesis generation algorithm.
Launch process
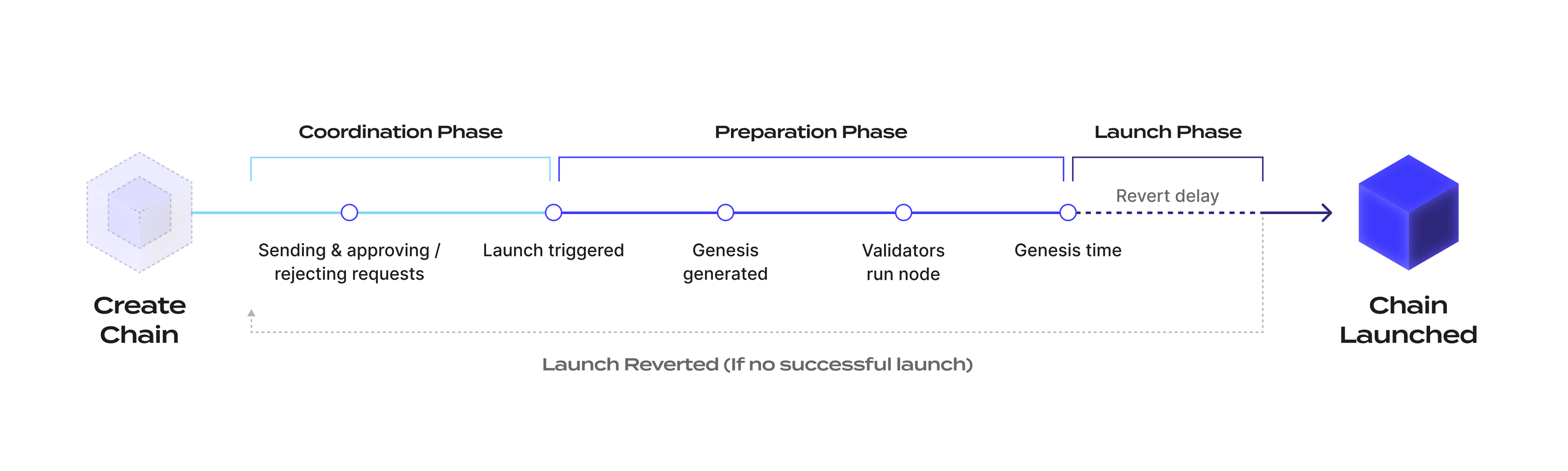
The overall launch process of a chain through Ignite is composed of three phases:
- Coordination phase
- Preparation phase
- Launch phase
After the coordinator creates the chain on Ignite and provides the initial launch information, the launch process enters the coordination phase where users can send requests for the chain genesis. After the coordinator deems the chain as ready to be launched, they trigger the launch of the chain. During this operation, the coordinator provides the launch time, or genesis, time for the chain.
Once the launch is triggered and before the launch time is reached, the chain launch process enters the preparation phase. During the preparation phase, requests can no longer be sent and the launch information of the chain is finalized. The validators run the genesis generation algorithm to get the final genesis of the chain and prepare their node. The remaining time must provide enough time for the validators to prepare their nodes. This launch time is set by the coordinator, although a specific range for the remaining time is imposed.
Once the launch time is reached, the chain network is started and the chain launch process enters the launch phase. At this point, since the chain is live, no further action is required from the coordinator. However, under some circumstances, the chain might have failed to start. For example, a chain does not start if every validator in the genesis does not start their node.
The coordinator has the ability to revert the chain launch. Reverting the chain launch sets the launch process back to the coordination phase where requests can be sent again to allow addressing the issue related to the launch failure. Reverting the launch has an effect only on Ignite. If the new chain is effectively launched, reverting the launch on Ignite has no effect on the chain liveness. Reverting the launch of the chain can be performed only by the coordinator after the launch time plus a delay called the revert delay.
Genesis generation
To ensure determinism, genesis generation rules must be rigorously specified depending on the launch information of the chain.
The general steps for the genesis generation are:
- Building the blockchain node binary from source
- Generating the initial genesis
- Setting the chain ID
- Setting the genesis time
- Adding genesis accounts
- Adding genesis accounts with vesting options
- Adding gentxs for genesis validators
- Changing module params from param changes